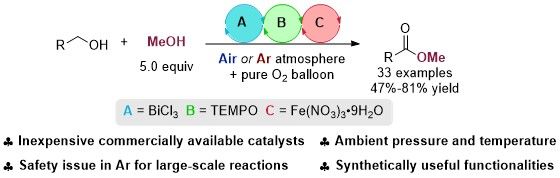
Esters are bulk and fine chemicals and ubiquitous in polymers, bioactive compounds, and natural products. Traditional approach is the esterification of carboxylic acids or their activated derivatives with alcohols. Herein, a bimetallic relay catalytic protocol has been developed for the aerobic esterification of one alcohol in the presence of a slowly oxidizing alcohol, which has been identified as methanol. Mechanistic studies exclude the possibility of esterification of in situ generated carboxylic acid with methanol and reveal that BiCl3 plays a critical dual role both in the oxidation of the alcohols to aldehydes and the subsequent formation of the semi-acetals, which would be further oxidized to form the final methyl carboxylates. A 100 mmol-scale reaction and a concise synthesis of phlomic acid have been executed to demonstrate the practicality and potential of this reaction.